What are Diecast Models?
Diecast models are miniature vehicles or figures created using a manufacturing process called die casting. This involves injecting molten metal, typically zinc alloys, into molds. The resulting models are known for their durability and intricate detail, making them a popular choice for collectors and enthusiasts. They are often made of metal, typically steel or a zinc alloy, which gives them a substantial weight and a realistic feel. The die-casting process allows for complex designs and detailed features, which is a significant advantage for replicating the look of real-life vehicles or figures. Diecast models have a rich history and are highly valued for their quality and collectibility, offering a tangible connection to automotive history and design.
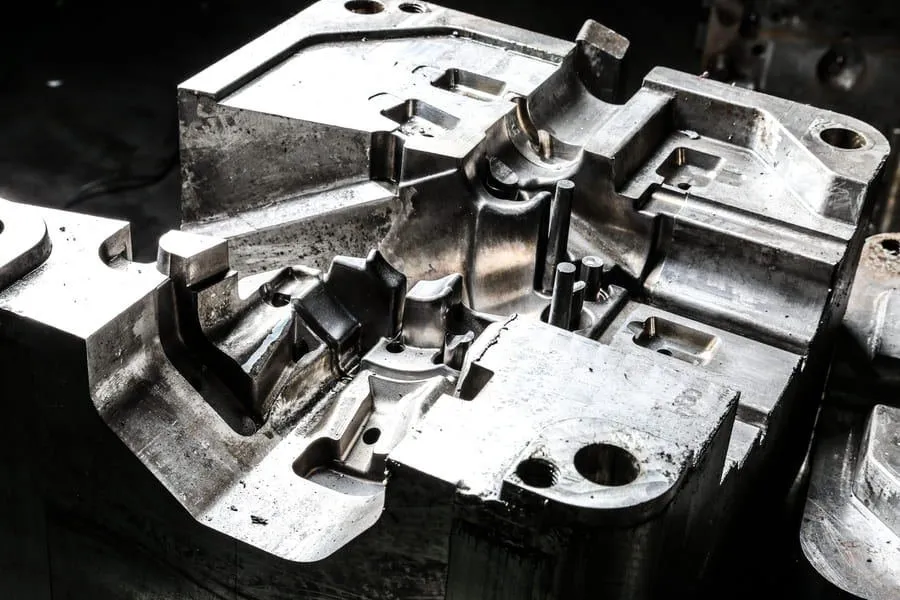
The Diecast Model Production Process
The production of diecast models is a meticulous process. It begins with the creation of molds, which are typically made of steel. These molds are precisely designed to capture every detail of the model. Molten metal, often a zinc alloy, is injected into these molds under high pressure. This process ensures that the metal fills every intricate part of the mold, accurately reproducing the desired shape. Once the metal cools and solidifies, the models are removed from the molds. The next stages include cleaning, trimming, and finishing the models. This may involve removing any excess material, smoothing surfaces, and preparing them for painting. Finally, the models are painted and assembled, often with additional details like decals and interior components. Quality control is crucial throughout the entire process to ensure that each model meets the high standards of accuracy and detail that collectors expect. Each stage requires precision and attention to detail, from the initial design to the final assembly.
Materials Used in Diecast Models
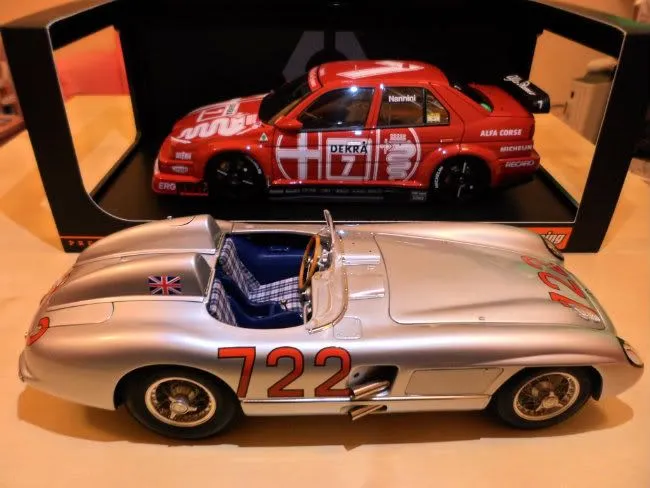

The primary material used in diecast models is a zinc alloy. This alloy, often called Zamak, is favored for its excellent casting properties, strength, and ability to capture fine details. Zamak’s low melting point makes it easy to work with during the die-casting process, allowing intricate designs to be created. Other materials are used to complement the metal components. These include plastic for parts such as tires, interior components, and windows. Rubber may also be used for tires. Paint, decals, and various adhesives complete the model. The choice of materials ensures that diecast models are both durable and visually appealing, accurately replicating real-world vehicles or figures. The combination of metal and plastic allows for both the weight and feel of a real vehicle and the fine details that enhance the model’s appearance.
Advantages of Diecast Models
Diecast models offer several advantages. Their durability is a significant benefit. The metal construction makes them resistant to damage, and they can withstand handling and display over many years. They are often more affordable than resin models, making them accessible to a wider range of collectors. The die-casting process allows for high-volume production, which contributes to lower production costs and greater availability. The detail and accuracy of diecast models are also notable. Manufacturers can reproduce complex designs with precision, capturing the nuances of the original vehicle. The weight of the models also adds to their appeal, giving them a realistic feel. The combination of these factors makes diecast models an excellent choice for collectors who value both quality and affordability. They are an accessible and durable option for enthusiasts of all ages.
What are Resin Models?
Resin models are scale replicas crafted from a synthetic resin material. Unlike diecast models, they are not made from metal. Resin models are typically produced using molds, where liquid resin is poured into the mold and allowed to cure. This process allows for intricate details and complex designs, appealing to serious collectors. Resin models often feature highly detailed features, offering a premium collecting experience. The use of resin allows for greater flexibility in design and detailing. These models are popular among collectors who seek high-quality, accurate representations of vehicles or figures. The resin material can be easily shaped and molded, allowing for detailed replicas that are difficult to achieve with traditional die-casting methods. Resin models often cater to niche interests and offer collectors a more exclusive option.
The Resin Model Production Process
The creation of resin models begins with the creation of molds, often made from silicone rubber. The molds are designed to capture fine details. Liquid resin is then carefully poured into the molds. The resin hardens or cures, typically through a chemical reaction. This process takes time, and the curing process may vary depending on the type of resin used. Once the resin has fully cured, the model is removed from the mold. The models then undergo a finishing process that involves cleaning, trimming, and sanding. This is done to remove any imperfections or excess material. Finally, the model is painted and assembled, often with intricate details and finishing touches. Quality control is an essential aspect of the resin model production process, ensuring that each model meets the high standards of accuracy and detail expected by collectors. This detailed process yields highly accurate and detailed models.
Materials Used in Resin Models
The primary material used in resin models is, unsurprisingly, resin. Various types of synthetic resins are used, offering different properties in terms of detail, strength, and finish. Polyurethane resin is a common choice, known for its ability to capture intricate details. Other materials used include paints, primers, and adhesives. Plastics may be used for transparent parts, such as windows or lights. Decals and photo-etched parts are often added to increase realism. The selection of materials is critical to the quality and accuracy of the final product. The materials used contribute to both the visual appeal and durability of the model. Resin models showcase a wide range of details due to the flexibility of the resin material. Careful selection of materials ensures that each model accurately represents its real-world counterpart.
Advantages of Resin Models
Resin models offer several advantages, including superior detail and accuracy. The molding process allows for intricate designs, capturing the nuances of the original vehicle or figure. Resin models are often used for limited production runs, making them more exclusive and sought after by collectors. They also allow for a greater level of customization, enabling manufacturers to produce specialized versions and variations. This level of detail and exclusivity makes resin models popular among serious collectors. Resin models are often preferred for their ability to replicate fine details and complex shapes. The use of resin allows for a high degree of design flexibility. This is especially important when replicating unique or rare vehicles. Resin models offer enthusiasts a premium collecting experience.
Key Differences Between Diecast and Resin Models

The main difference lies in the materials and the manufacturing process. Diecast models are made from metal, typically a zinc alloy, using a die-casting process. Resin models are made from synthetic resin poured into molds. The construction of diecast models usually involves several parts that are assembled together, whereas resin models tend to be made from fewer parts. This affects the level of detail and the complexity of the design. Diecast models are generally more durable and heavier due to their metal construction. Resin models can offer greater detail and accuracy, making them ideal for replicating complex designs. The production volume and cost also differ; diecast models often have higher production volumes, which lowers their cost. Resin models are typically produced in smaller quantities, which increases their price. Ultimately, the choice between a diecast and a resin model comes down to the preferences of the collector. Each type of model has its unique strengths and appeals to different enthusiasts.
Material and Construction
Diecast models are primarily metal, making them sturdy and heavy. Their construction involves assembling various parts. Resin models are made of resin, making them lighter and allowing for intricate detailing. The material differences significantly impact the feel and look of the models.
Detail and Accuracy
Resin models often excel in detail and accuracy due to the molding process. They can capture fine details. Diecast models also provide high detail levels, though the process may limit some aspects. The choice depends on the level of detail you are looking for.
Durability and Weight
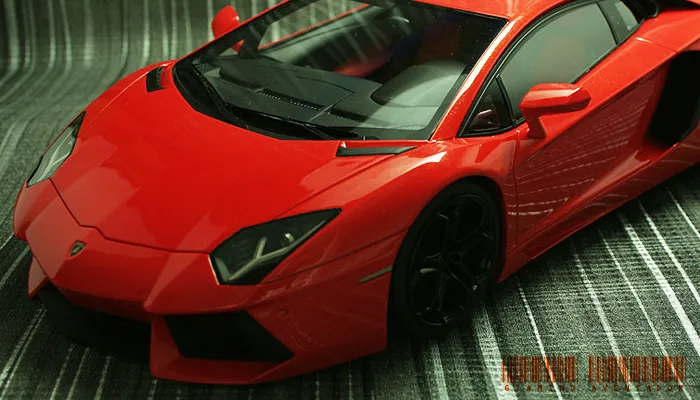

Diecast models are known for their durability because of the metal construction. They can withstand handling and display. Resin models can be more fragile and require careful handling. Weight differences are noticeable; diecast models are heavier.
Production Volume and Cost
Diecast models are often produced in larger quantities, resulting in lower production costs. This makes them more affordable. Resin models have limited production runs, resulting in higher prices, but they are more exclusive.
Price and Availability
Diecast models are more readily available and often less expensive. Their higher production volumes make them easy to find. Resin models are usually more expensive and may be available through specialist retailers. Availability is often limited to specific model lines or variations.
Which Model is Right for You?

The right model for you depends on your preferences and collecting goals. Consider your budget, the level of detail you desire, and how you plan to display and handle your models. If you value durability and affordability, diecast models may be the better choice. If you prioritize intricate details and exclusivity, resin models might be more appealing. Exploring both types and understanding their characteristics can help you make an informed decision and build a collection that meets your needs.
Factors to Consider When Choosing
Several factors should be considered before choosing between diecast and resin models. Consider your budget, as diecast models are typically more affordable. Think about the desired level of detail; if you want intricate features, resin might be better. Evaluate the model’s purpose, whether for display or play; diecast models are more durable. Reflect on your personal collecting goals and the type of models you want to add to your collection. Look at availability and consider that resin models might be harder to find.
Diecast Models Ideal For
Diecast models are ideal for collectors looking for affordability and durability. They are great for those new to the hobby due to their lower cost. Collectors who want models that can withstand handling and display over many years will appreciate diecast models. They are suitable for those who are looking for a broad range of models, as diecast models are widely available. They’re also suitable for children and those who prioritize play over highly detailed aesthetics.
Resin Models Ideal For
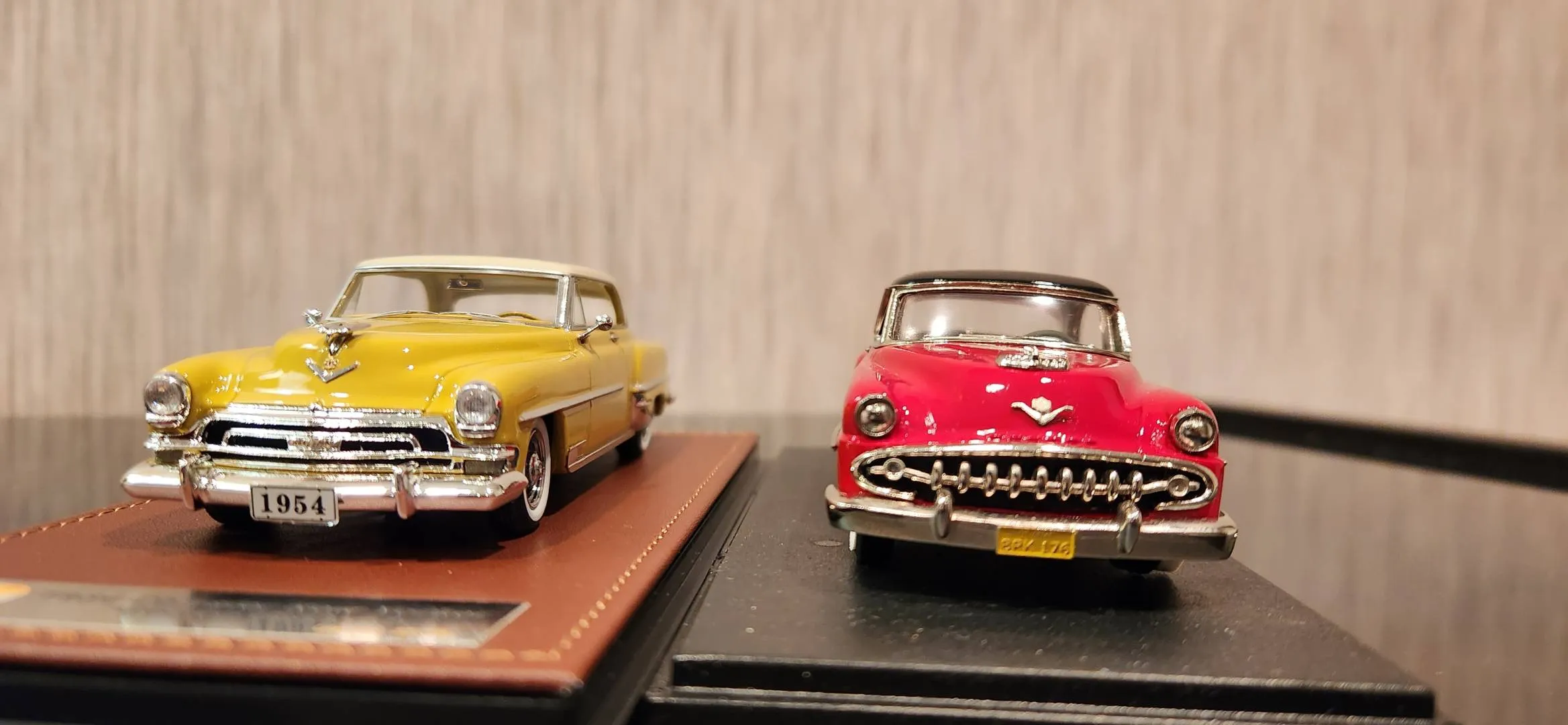

Resin models are ideal for collectors prioritizing detail and accuracy. Those who want high-end models with intricate details will find resin models appealing. They are perfect for collectors willing to spend more for exclusive models. They cater to those who appreciate a high level of design and are willing to handle the models with care. Resin models are also suitable for collectors who want limited edition pieces. They often represent rare or unique vehicles.
