Diecast vs Resin Models
The world of model cars offers a vast array of choices for collectors and enthusiasts. Among the most popular types are diecast and resin models. Both aim to replicate real-life vehicles in miniature form, but they differ significantly in their materials, manufacturing processes, detail levels, and overall characteristics. Understanding these differences is crucial for anyone looking to start or expand their collection, as it will influence the type of models you choose to acquire and appreciate. This guide will explore the top 5 key differences between diecast and resin models to help you make informed decisions.
Material Composition
The primary distinction between diecast and resin models lies in their materials. This fundamental difference affects all other aspects, from the production process to the final product’s feel and appearance. The material composition dictates the model’s weight, durability, and level of detail. Recognizing these material characteristics is the first step in differentiating between the two types of models.
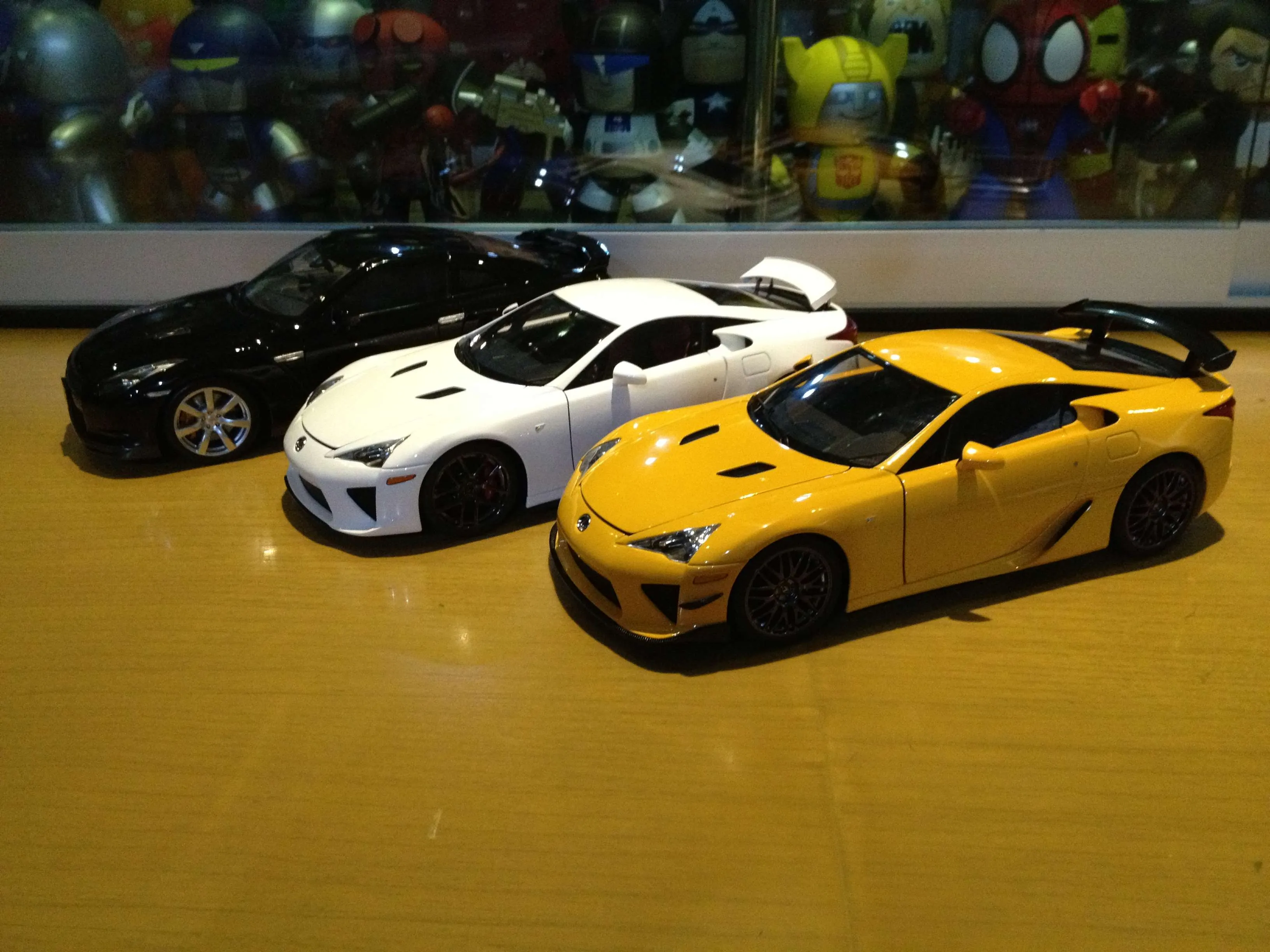
Diecast

Diecast models are predominantly made from a zinc alloy, often mixed with other metals like tin and copper. This alloy is melted and injected into molds under high pressure, hence the name ‘diecast’. The use of metal gives diecast models a substantial weight and a cool, solid feel. This weight contributes to the realism of the model, making it feel more like a scaled-down version of a real car. Diecast models often include plastic and rubber components for details like tires, interior elements, and some exterior features.
Resin
Resin models, on the other hand, are crafted from a synthetic resin material. This is a liquid polymer that hardens when cured, usually through a chemical process or exposure to UV light. Resin models often use a polyurethane resin, allowing for intricate details and smooth surfaces. Resin’s properties enable manufacturers to create complex shapes and fine details that might be challenging or impossible to achieve with diecast methods. Resin models also tend to be lighter than their diecast counterparts.
Manufacturing Process
The manufacturing processes for diecast and resin models are vastly different, influencing the types of details achievable and the overall production costs. Each method has its advantages and disadvantages, which contribute to the final product’s unique characteristics. The production techniques also influence the price point and availability of various models.
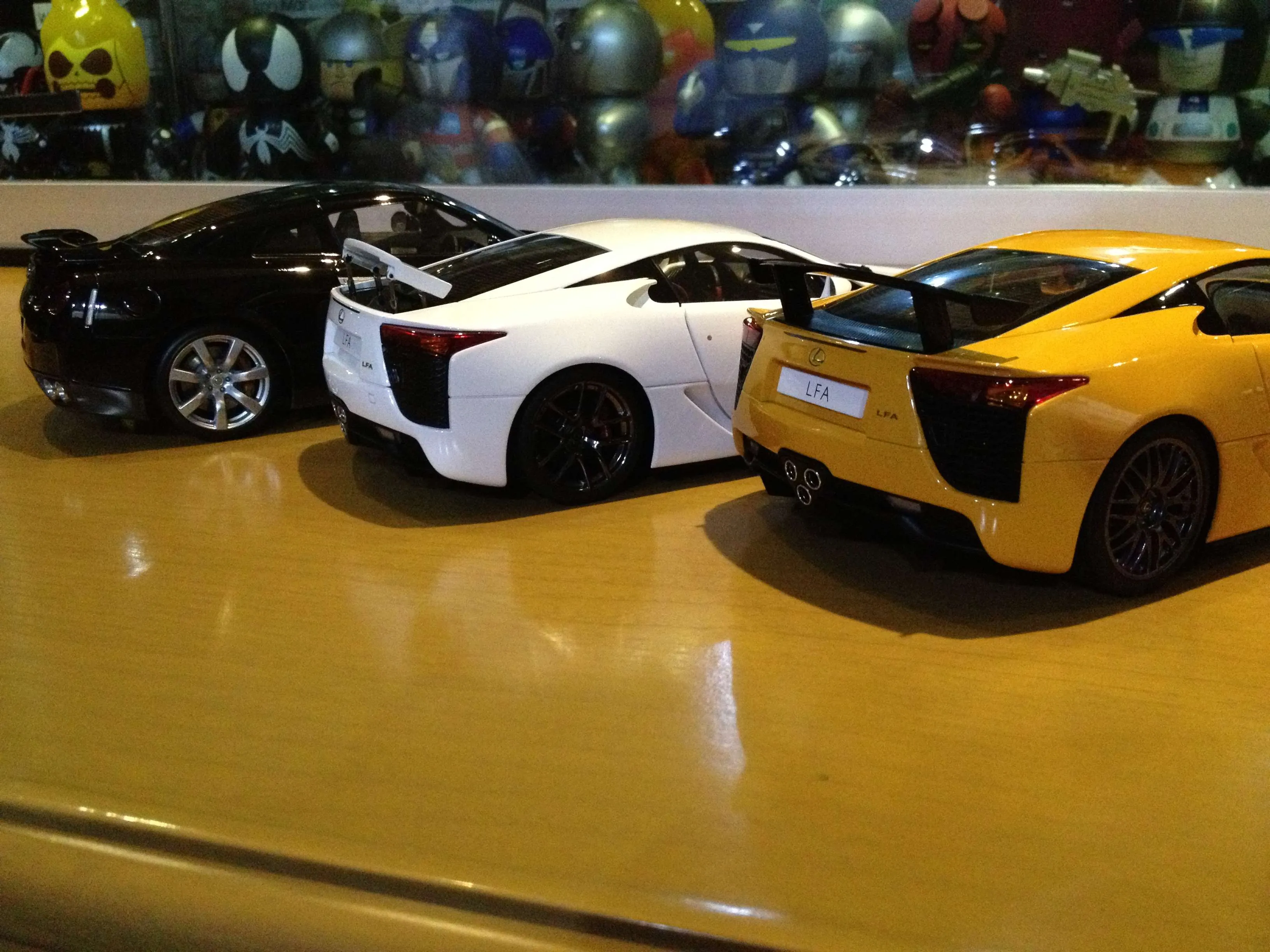
Diecast

Diecast models are made using a process where molten metal is injected into steel molds under high pressure. This ‘die casting’ method allows for high-volume production and relatively lower production costs. The molds are typically made in two or more parts that are joined together. After the metal cools and solidifies, the model is removed, and the excess metal is trimmed. Diecast models often require multiple steps, including painting, detailing with plastic components, and assembling the various parts. This process, although efficient, may have limitations in detail complexity.
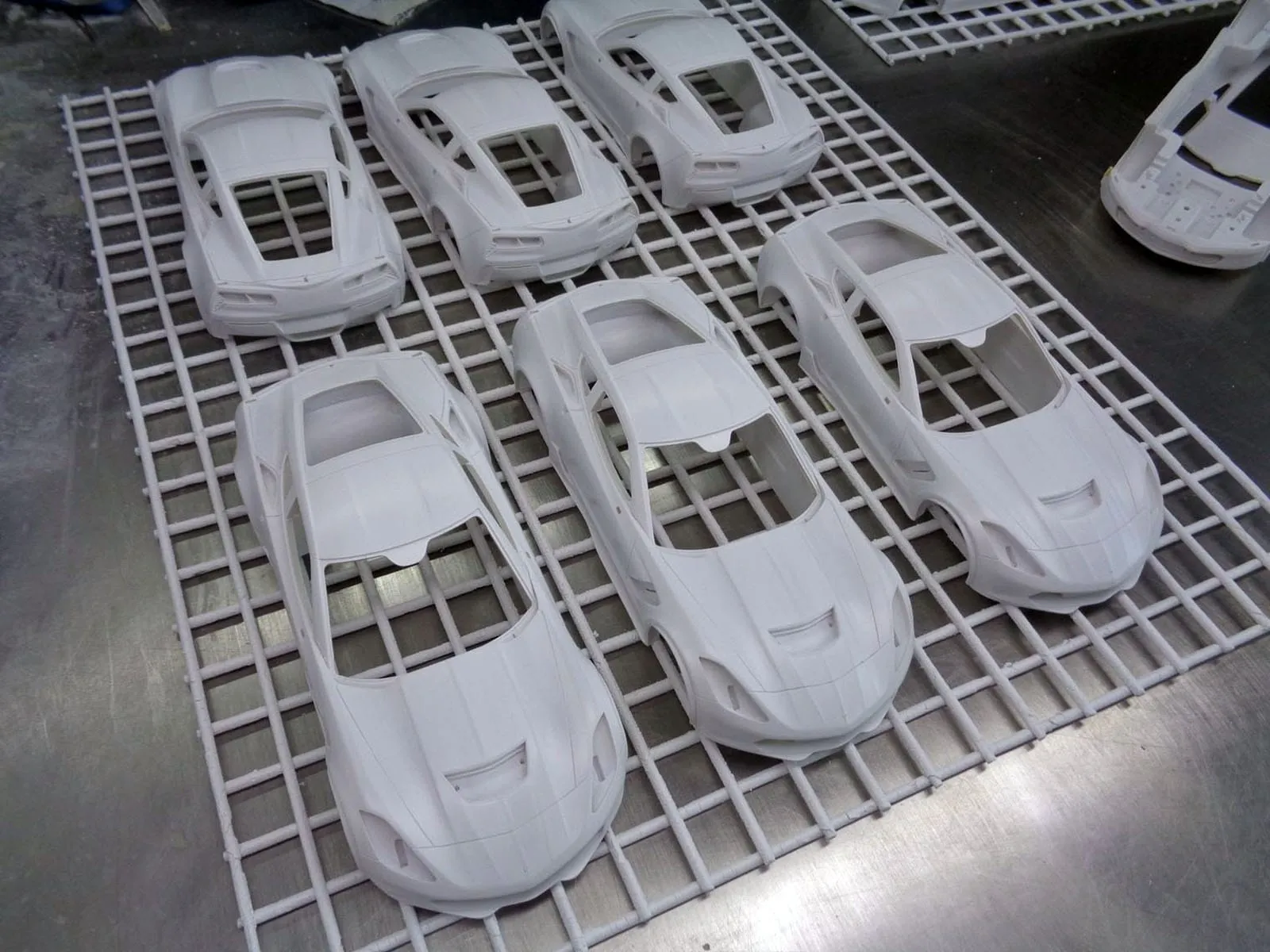
Resin
Resin models are typically manufactured using a mold-casting process. Liquid resin is poured into a mold, often made from silicone rubber. The resin cures and hardens within the mold, replicating the mold’s details. This process allows for highly detailed parts and intricate designs. Resin models are often assembled by hand, with individual components being glued together. While mold-casting can produce complex shapes, it’s generally a slower and more labor-intensive process than diecasting, which results in higher production costs.
Detail and Accuracy
Detail and accuracy are critical aspects of model car collecting. The level of detail determines how closely the model replicates the real-life vehicle. Both diecast and resin models strive for accuracy, but their manufacturing processes lead to different strengths and weaknesses in this area. The choice between the two often comes down to the level of detail desired by the collector.
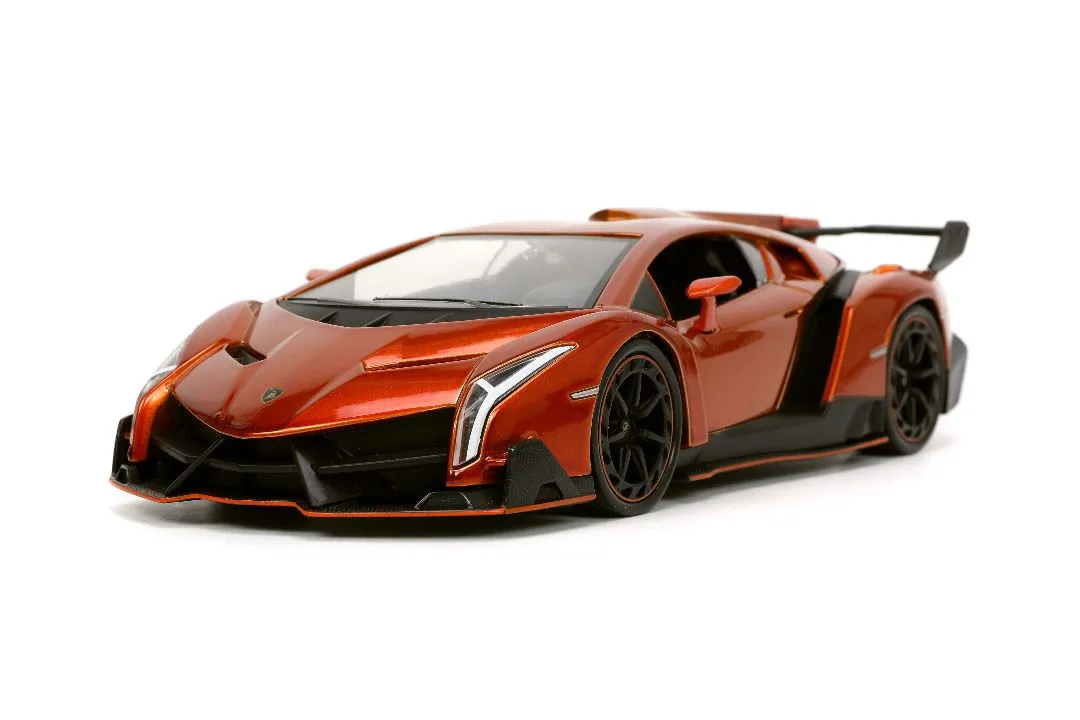
Diecast

Diecast models have improved significantly over time in terms of detail. Modern diecast models can feature highly detailed interiors, realistic paint finishes, and accurately replicated exterior features. However, the diecasting process has inherent limitations. Certain features, such as fine grilles, delicate trim, or intricate body lines, can be more challenging to reproduce perfectly. Diecast models often have working features like opening doors, hoods, and steering wheels, enhancing playability and collectibility.
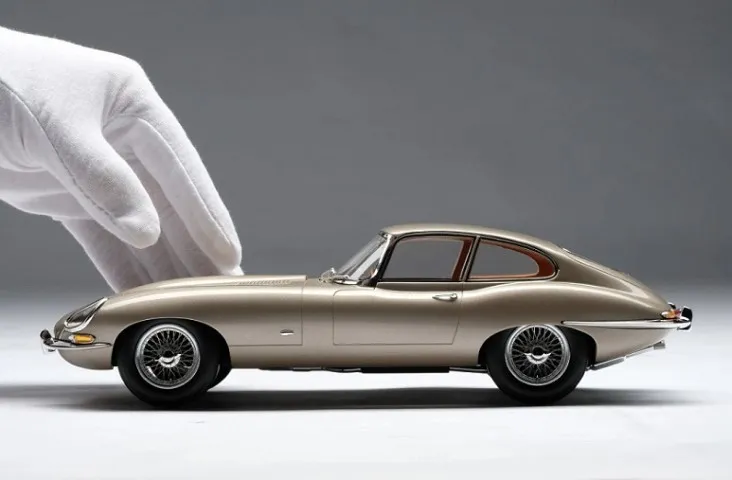
Resin
Resin models are often praised for their exceptional detail and accuracy. The mold-casting process allows for the creation of incredibly fine details, intricate body lines, and complex features that might be difficult or impossible to achieve with diecast methods. Resin models can often include features like photo-etched parts for grilles, detailed dashboards, and ultra-thin window frames. The high level of detail makes resin models especially attractive to serious collectors who prioritize realism and accuracy. Resin models typically lack moving parts to maintain their integrity and detail.
Durability and Weight
Durability and weight significantly impact the feel and longevity of a model car. These factors also influence how a model can be displayed, stored, and handled. The materials and manufacturing techniques used to create diecast and resin models contribute to noticeable differences in their durability and weight.
Diecast
Diecast models are generally more durable than resin models due to the robustness of the metal alloy used in their construction. They can withstand more handling and are less susceptible to damage from accidental drops or impacts. The weight of diecast models gives them a solid feel, enhancing the perception of quality. However, the paint on diecast models can be susceptible to chipping or scratching, especially around moving parts.
Resin
Resin models, while often highly detailed, tend to be more fragile than diecast models. The resin material can be more brittle, and they are more susceptible to breakage if dropped or mishandled. The lighter weight of resin models can make them feel less substantial. They are often better suited for display than for extensive handling. Collectors need to handle resin models with greater care to preserve their condition.
Cost and Availability
The cost and availability of diecast and resin models vary, reflecting the materials, manufacturing processes, and levels of detail involved. This section explores how these factors influence the price and ease of acquiring these model cars.
Diecast

Diecast models are generally more affordable than resin models. Their mass-production techniques and use of relatively inexpensive materials contribute to a lower price point. This makes them accessible to a broader range of collectors, from beginners to seasoned enthusiasts. Diecast models are also more widely available, often found in various stores, online retailers, and hobby shops. The variety of diecast models allows for a wider range of choices to suit various budgets and preferences.
Resin
Resin models typically come at a higher price due to the more labor-intensive production process and the use of specialized materials. The limited production runs for resin models also contribute to their higher cost. Resin models are often considered premium collectibles, reflecting their higher levels of detail and exclusivity. They can be harder to find and may be available primarily through specialist retailers or online marketplaces. The higher price point often caters to serious collectors who prioritize detail and rarity.
Conclusion
Choosing between diecast and resin models depends on your individual preferences, budget, and collecting goals. Diecast models offer durability, affordability, and a wider range of options, making them ideal for beginners and collectors who enjoy handling their models. Resin models excel in detail and accuracy, appealing to serious collectors who prioritize realism and are willing to invest in premium collectibles. Consider the factors discussed to determine which type of model best suits your needs, and happy collecting!
